What Is The Role Of Wildlife Conservancies In Kenya?
In Kenya, wildlife conservancies play a crucial role in preserving the country’s rich biodiversity and ensuring the survival of endangered species. These conservancies serve as protected areas, providing safe havens for wildlife to thrive and flourish. By adopting sustainable conservation practices and promoting eco-tourism, wildlife conservancies not only safeguard the natural habitats but also contribute to the socio-economic development of local communities. Discover the significant contributions of wildlife conservancies in Kenya and how they are shaping the future of conservation efforts in the region.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Protecting Endangered Species
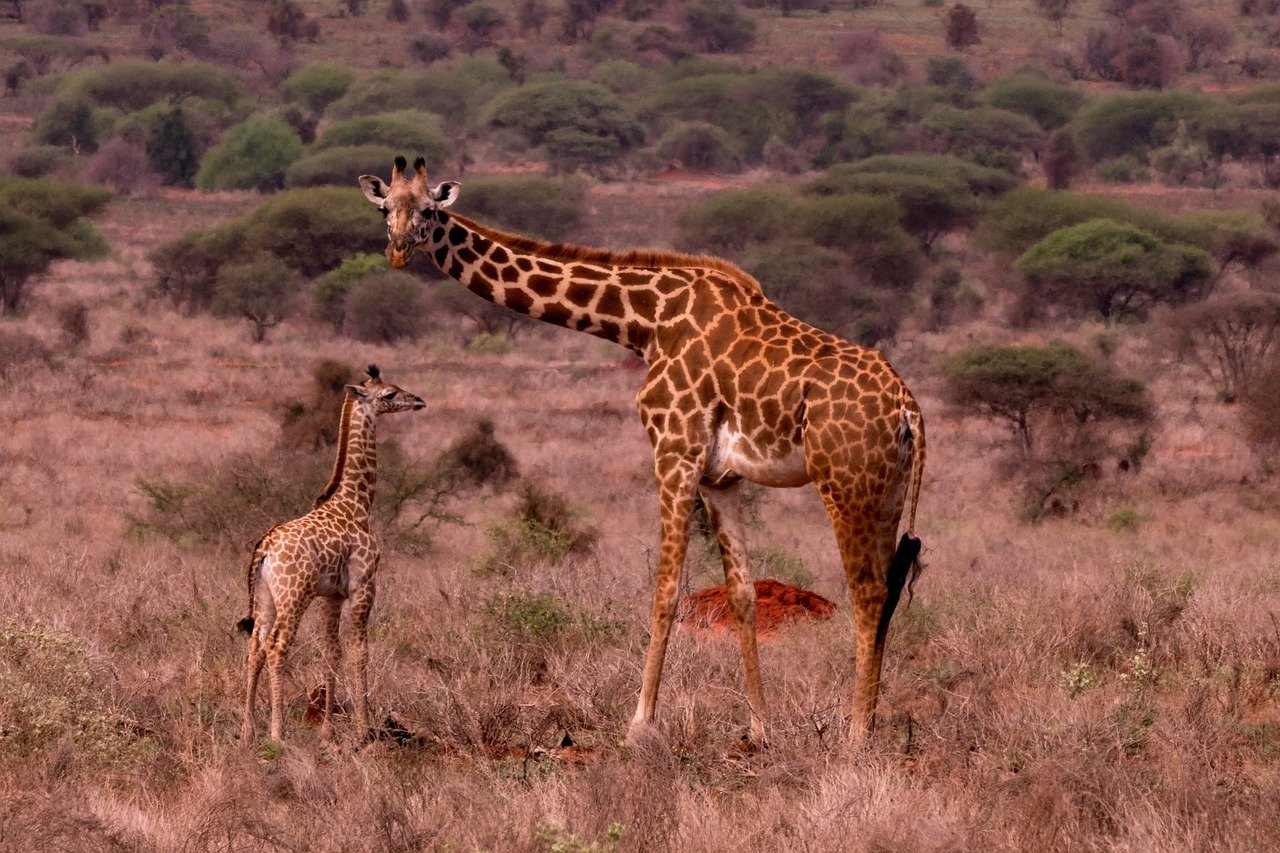
One of the primary roles of wildlife conservancies in Kenya is the protection of endangered species. These conservancies serve as safe havens for animals that are at risk of extinction. By preserving their natural habitats and implementing rigorous anti-poaching measures, conservancies ensure that endangered species, such as elephants, rhinos, and lions, have a conducive environment to thrive. Through careful monitoring and conservation efforts, these conservancies contribute significantly to the recovery and survival of species with declining populations.
Preserving Threatened Habitats
In addition to safeguarding endangered species, wildlife conservancies in Kenya play a vital role in preserving threatened habitats. These conservancies work diligently to maintain the integrity of ecosystems, such as savannas, wetlands, and forests, which are crucial for the survival of countless plant and animal species. By preventing habitat destruction, conservancies protect biodiversity and ensure the long-term viability of ecosystems that are under threat from factors like deforestation, human encroachment, and climate change.
Community Development
Creating Employment Opportunities
Wildlife conservancies in Kenya contribute to community development by creating employment opportunities for local residents. These conservancies often employ community members as wildlife rangers, guides, lodge staff, and conservation officers. By offering these jobs, conservancies provide income and stability to individuals and families in rural areas. This not only alleviates poverty but also reduces the reliance on activities that may be harmful to the environment, such as illegal poaching and logging.
Supporting Livelihoods
In addition to direct employment, wildlife conservancies also support local livelihoods through various initiatives. They collaborate with communities to develop sustainable tourism activities that provide additional income options, such as cultural tourism experiences, eco-lodges, and handicraft sales. By diversifying income sources, conservancies help communities become more resilient to economic fluctuations and reduce dependence on unsustainable practices like agriculture and livestock grazing, which can degrade natural habitats.
Enhancing Education and Healthcare
Wildlife conservancies recognize the importance of education and healthcare in empowering local communities. Many conservancies invest in education programs, including scholarships, vocational training, and environmental education initiatives. By improving access to quality education, conservancies equip community members with the skills and knowledge needed for better employment prospects and future conservation efforts.
Similarly, wildlife conservancies often partner with local health organizations to improve healthcare facilities and services in rural areas. They may provide medical supplies, support the construction of clinics, or facilitate healthcare outreach programs. By prioritizing education and healthcare, conservancies contribute to the overall well-being and sustainability of local communities.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Promotion of Sustainable Tourism
Attracting Tourists
Wildlife conservancies in Kenya play a significant role in attracting tourists by offering unique and immersive wildlife experiences. These conservancies provide visitors with opportunities to view iconic African wildlife species in their natural habitats, away from overcrowded national parks. They offer activities like game drives, guided walks, photography tours, and cultural interactions, which create memorable experiences for tourists seeking a closer connection with nature.
Generating Revenue
Sustainable tourism promoted by wildlife conservancies generates substantial revenue for local communities and conservation efforts. Income from conservancy fees, accommodation, food, and related services directly supports the operations and maintenance of conservancies. The revenue generated also circulates within the local economy, benefiting businesses ranging from restaurants and shops to transportation providers and artisans. This economic flow helps stimulate growth, generate employment, and improve living standards for communities living adjacent to the conservancies.
Preserving Cultural Heritage
Apart from their ecological significance, wildlife conservancies also play a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage. Many conservancies are located in regions inhabited by indigenous communities that have deep-rooted connections to the land and its wildlife. Through collaborative efforts, these conservancies work with local communities to revive cultural practices, traditions, and craftsmanship related to wildlife conservation. By celebrating and preserving cultural heritage, conservancies ensure the continuation of unique cultural identities, while also promoting cross-cultural understanding among visitors.
Conflict Mitigation
Reducing Human-Wildlife Conflicts
One of the challenges faced in wildlife conservation is human-wildlife conflicts, where local communities clash with wildlife due to damage to crops, livestock, or threat to human lives. Wildlife conservancies in Kenya actively work towards reducing such conflicts by implementing various strategies. They engage in community-based conservation programs that provide measures like secure fencing, early warning systems, and compensation schemes for losses incurred. These initiatives help prevent conflicts, ensuring that both local communities and wildlife can coexist harmoniously.
Promoting Coexistence
In addition to conflict reduction, wildlife conservancies promote coexistence between humans and wildlife by raising awareness and promoting understanding. They organize educational workshops, community meetings, and awareness campaigns to foster empathy and knowledge about the importance of wildlife conservation. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and showcasing the benefits of conservation, conservancies encourage a sense of shared responsibility for the protection of wildlife and the preservation of their habitats.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
Research and Monitoring
Collecting Data on Wildlife Populations
Wildlife conservancies contribute significantly to research and monitoring efforts by collecting valuable data on wildlife populations. Through ongoing surveys, camera trapping, GPS tracking, and collaring programs, conservancies provide critical information to conservation scientists and organizations. These data help monitor population trends, assess the success of conservation measures, and guide future strategies for wildlife management. By actively participating in data collection, wildlife conservancies contribute to the broader scientific understanding of biodiversity and aid evidence-based conservation decisions.
Studying Behavioral Patterns
Alongside population data, wildlife conservancies also contribute to the study of behavioral patterns of various species. By closely observing animal behavior, conservancies gather insights into social structures, feeding patterns, migration routes, and breeding habits. This knowledge is invaluable in guiding conservation efforts, as it allows researchers to identify and address the specific needs and challenges faced by different species. Understanding these behavioral patterns aids in the development of targeted conservation interventions to protect wildlife and their habitats effectively.
Monitoring Conservation Efforts
Lastly, wildlife conservancies in Kenya actively monitor their own conservation efforts to assess their impact and effectiveness. They track key indicators such as poaching rates, habitat restoration progress, and species recovery. By regularly evaluating their initiatives, conservancies can identify areas for improvement and adapt conservation strategies accordingly. This self-assessment and monitoring ensure the continuous refinement of conservation practices, leading to more efficient wildlife management and increased success in preserving biodiversity.
Community Engagement
Involving Local Communities in Conservation Programs
Community engagement lies at the heart of wildlife conservancies in Kenya. These conservancies believe in the importance of involving local communities in conservation programs. They establish partnerships with community representatives and elders to incorporate traditional knowledge and practices into conservation efforts. By including local communities in decision-making processes, conservancies foster a sense of ownership and stewardship towards the natural resources and wildlife. This involvement ensures that conservation initiatives align with the needs and aspirations of community members, strengthening the overall effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Raising Awareness
Wildlife conservancies actively engage in raising awareness among local communities about the importance of wildlife conservation. They conduct workshops, educational programs, and public campaigns to highlight the ecological, economic, and cultural significance of conserving biodiversity. By educating community members about the interconnectedness of all living beings and the role they can play in conservation, conservancies empower individuals to actively participate in safeguarding their natural heritage.
Building Partnerships
Wildlife conservancies understand the importance of collaboration and building partnerships to achieve sustainable conservation outcomes. They work closely with local authorities, community-based organizations, NGOs, and government agencies to pool resources, share knowledge, and coordinate strategies. These partnerships enhance the capacity of conservancies to address complex conservation challenges effectively and drive positive change at both local and national levels. By fostering collaboration, wildlife conservancies create a network of stakeholders committed to the shared goal of protecting biodiversity.
Ecosystem Restoration
Rehabilitating Degraded Land
Wildlife conservancies in Kenya actively participate in ecosystem restoration by rehabilitating degraded land. They engage in initiatives like reforestation, soil erosion control, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. By restoring natural habitats and improving degraded ecosystems, conservancies create a healthier environment for wildlife to thrive. Ecosystem restoration also benefits local communities by enhancing soil fertility, promoting water retention, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Reintroducing Native Species
In addition to restoring habitats, wildlife conservancies also contribute to the reintroduction of native species. Species that were previously extirpated or locally extinct due to various factors, such as hunting or habitat loss, are being reintroduced into protected areas by conservancies. These reintroduction programs serve to restore ecological balance, enrich biodiversity, and strengthen ecosystems. By actively participating in these programs, conservancies play a critical role in restoring the natural heritage of Kenya and ensuring the long-term survival of native species.
Preserving Natural Resources
Protecting Water Sources
Wildlife conservancies prioritize the protection of water sources as a crucial aspect of conservation efforts. They implement measures to prevent water pollution, regulate water usage, and restore degraded water bodies. By safeguarding freshwater sources, conservancies ensure the availability of clean water for both wildlife and local communities, promoting overall ecosystem health and resilience.
Maintaining Soil Quality
Conserving soil quality is another essential role played by wildlife conservancies in Kenya. They adopt sustainable land management practices, such as organic farming techniques and rotational grazing systems, to prevent soil erosion and degradation. By maintaining healthy soil, conservancies support agricultural productivity, enable natural vegetation growth, and facilitate the availability of essential nutrients for plant and animal life.
Conserving Forests
Lastly, wildlife conservancies contribute to the conservation of forests, which provide critical habitats for numerous species and offer a range of ecosystem services. They collaborate with local communities to prevent illegal logging, protect forested areas from encroachment, and promote sustainable forestry practices. Forest conservation efforts by conservancies help maintain biodiversity, regulate climate, and support the livelihoods of communities dependent on forest resources like non-timber forest products (NTFPs) and ecotourism activities.
Climate Change Mitigation
Carbon Sequestration
Wildlife conservancies actively contribute to climate change mitigation through carbon sequestration. By conserving forests and other carbon-rich ecosystems, conservancies help absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Forests, in particular, act as crucial carbon sinks, capturing significant amounts of greenhouse gases. Protecting and restoring these ecosystems through conservancies helps reduce the overall carbon footprint, combat climate change, and preserve the ecological balance of the planet.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
In addition to carbon sequestration, wildlife conservancies also prioritize efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. They implement sustainable land management practices, encourage renewable energy adoption, and promote eco-friendly practices among local communities and visitors. Through these initiatives, conservancies not only contribute to global climate change mitigation efforts but also inspire individuals and communities to take steps towards a more sustainable future.
Enhancing Environmental Education
Educating Local Communities
Wildlife conservancies recognize the importance of environmental education in promoting conservation awareness and action. They invest in educational programs that target local communities, providing them with knowledge about the natural environment, wildlife, and sustainable conservation practices. Through workshops, school programs, and community engagement activities, conservancies empower individuals to make informed decisions and take actions that contribute to the preservation of biodiversity.
Promoting Conservation Awareness
In addition to education, wildlife conservancies actively promote conservation awareness among local communities and visitors. They organize interactive events, nature walks, and interpretive tours to connect people with the beauty and significance of the natural world. By fostering a sense of wonder and admiration for wildlife and their habitats, conservancies inspire individuals to become advocates for conservation and create a collective consciousness about the need to protect the environment.
In conclusion, wildlife conservancies in Kenya play a multifaceted and crucial role in conservation efforts. From protecting endangered species and preserving threatened habitats to promoting sustainable tourism and mitigating conflicts, these conservancies are at the forefront of preserving biodiversity and fostering coexistence between humans and wildlife. Through research, monitoring, and community engagement, they actively contribute to the understanding and conservation of wildlife. By prioritizing ecosystem restoration, the preservation of natural resources, and climate change mitigation, conservancies ensure the long-term sustainability of the environment. Lastly, by enhancing environmental education and promoting conservation awareness, they empower individuals and communities to become active participants in safeguarding Kenya’s rich natural heritage for future generations.